VPN Split Tunneling Explained: Benefits, Risks, And How to Use It?
Table of Contents
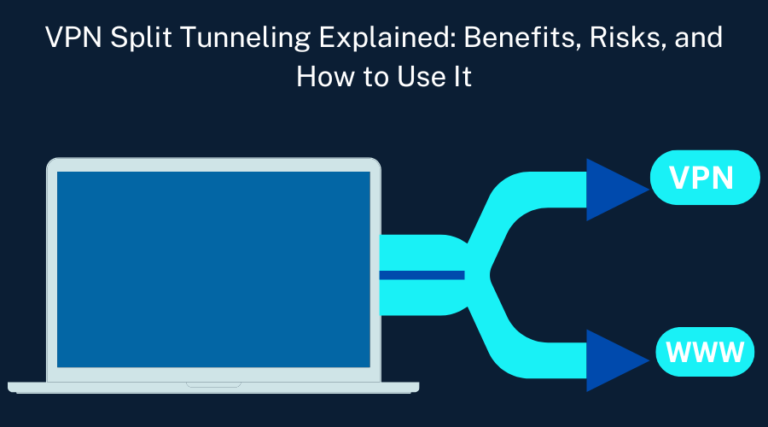
VPN split tunneling is a feature that allows the user to decide which internet traffic goes through your VPN and which goes directly through your regular internet connection. This means you can split your online activities, which apps or, better still, websites require the enhanced security and privacy of a VPN and which can go directly onto the Internet.
For example, you might consider routing your banking app’s connection via the VPN for security purposes or streaming apps to bypass the VPN, maintain faster speeds, and access content based on your preferred region.
This feature is useful when you want a VPN connection without losing speed or local service availability. It allows you to pass only the necessary traffic through the VPN, helping conserve bandwidth and improving performance.
However, it is important to know the process of VPN split tunneling to use it efficiently, as it is quite an important feature contributing to your online security and browsing efficiency.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know exactly what VPN split tunneling is, how it works, its benefits, and how you can use it safely to maximize your internet experience.
How Does VPN Split Tunneling Works?
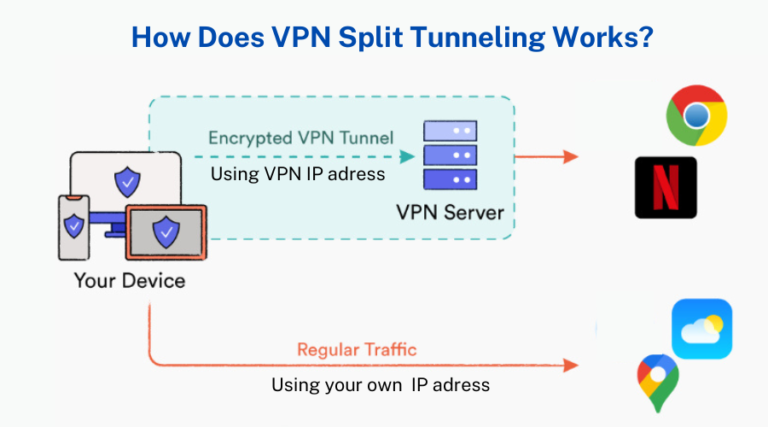
VPN split tunneling allows users to select which internet connections go through the VPN tunnel and which do not require VPN protection. Normally, when one logs into a VPN, his/her web traffic is routed to the VPN server through an encrypted path.
This protects your data and hides your IP address. However, with split tunneling, you can only make specific traffic through this secure VPN tunnel.
For example, if, in your work setup, you find that you have to open some company resources securely while the rest of their internet connection is quite fine as it is, you could allow only the specific traffic to go through the VPN.
At the same time, you’ll be able to complete all other operations, such as scrolling through social networks or streaming domestic platforms, on your ordinary connection with higher speed and less latency.
What are the Benefits of VPN Split Tunneling?
VPN split tunneling has benefits that make the feature useful to many users. Here’s a look at some key benefits:
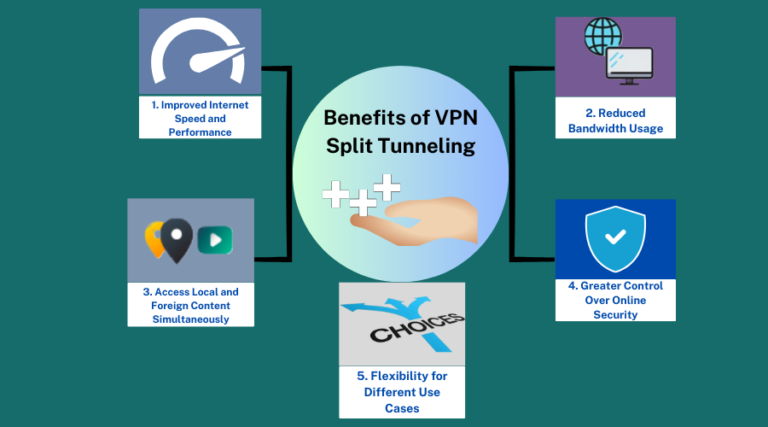
1. Improved Internet Speed and Performance
When all your traffic goes through a VPN, the connection speed may be reduced because of the encryption. This means that you can allow high bandwidth activities like streaming, gaming, and downloading through the normal network, not through the VPN, hence improving the activities while at the same time protecting your important information.
2. Reduced Bandwidth Usage
By routing only necessary traffic through the VPN, you reduce bandwidth consumption. This can be particularly handy using a limited data connection or a mobile device. For example, you can secure your work-related traffic with the VPN, while everyday browsing or local content doesn’t affect your data limit.
3. Access Local and Foreign Content Simultaneously
The split tunneling feature allows users to access local services and content while protecting other VPN traffic. For instance, you can watch local streaming services or access Websites that may block VPN connections while your work or financial data is secured under the VPN.
4. Greater Control Over Online Security
With split tunneling, you can decide exactly what needs to be protected. This feature is especially valuable for companies and remote workers who require secure access to company resources without compromising internet performance for other purposes.
5. Flexibility for Different Use Cases
Split tunneling allows VPN users to control their VPN tunnel settings according to their specific needs. This feature can be turned on and off to prevent certain applications or traffic from passing through, accessing local content, or improving VPN internet speed, making it an ideal VPN option.
VPN split tunneling can enhance your online experience by balancing security, performance, and accessibility, making it a valuable tool for anyone who uses a VPN regularly.
What Are the Security Risks associated with VPN Split Tunneling?
Earlier we have discussed about VPN Split tunneling benefits, it’s important to know the security risks associated with this feature. Here are some potential risks you should consider:
1. Exposure of Unencrypted Traffic
An important concern associated with split tunneling is that the traffic that goes through the VPN tunnel is only a part of the total traffic. The rest of the traffic is not tunneled and, therefore, is not encrypted.
This unprotected traffic can be problematic and is prone to cyber threats like hacking, spying, or interception of the transmitted data by undesired persons. For instance, if you are connecting through public WI-FI, any activity without a VPN connection can easily be intercepted.
2. Increased Risk of Data Leaks
Split tunneling can sometimes lead to data leaks if not configured properly. Sensitive information intended to be protected by the VPN could accidentally be exposed if the wrong apps or websites are excluded from the VPN tunnel. This misconfiguration can defeat the purpose of using a VPN for security and privacy.
3. Potential Vulnerability to Geo-Blocking and Censorship
Using split tunneling can make it easier for websites and services to detect your real IP address and location, especially if you’re accessing geo-restricted content. However, this could result in being blocked by websites or services that enforce strict regional restrictions or censorship, limiting your access to content.
4. Compromised Device Security
Sometimes, when some of the traffic does not go through the VPN connection, the device will likely be vulnerable to malware or phishing. Applications and services in other zones of the Internet can be attacked by cybercriminals, thus threatening the security of your device or data.
5. Reduced Overall Privacy
Split tunneling reduces the level of privacy you would typically get with a full VPN connection. Since not all traffic is hidden from your ISP or other prying eyes, your overall privacy can be diminished. This is especially concerning if you’re in a region with high surveillance or restrictive internet practices.
These are the security concerns that must be considered, as well as the measures that should be taken to decrease or prevent them. It is always important that all sensitive traffic go through the VPN and that the VPN be very selective about which application or service should not be encrypted by it.
How to Use VPN Split Tunneling?
VPN split tunneling allows users to selectively route internet traffic through a secure VPN connection or through a regular connection, ensuring network security and fast access to local services. Here’s a Step-by-Step Guide on how to use VPN split tunneling and make the most out of this feature:
1. Choose a VPN Service with Split Tunneling
Not all VPNs offer split tunneling, so it’s important to select a VPN provider that includes this feature. Popular options include NordVPN, Surfshark, and others that advertise split tunneling capabilities. Ensure your chosen VPN supports the devices and applications you plan to use.
2. Install and Set Up Your VPN
Download and install the VPN app on your device. Follow the setup instructions provided by the VPN provider. Once installed, log in to your account.
3. Access the Split Tunneling Settings
- On Desktop: In the VPN app, navigate to the settings or options menu. Look for a section labeled “Split Tunneling” or something similar.
- On Mobile: The process is similar on mobile devices. Open the VPN app, go to settings, and find the split tunneling option.
4. Select Which Traffic to Route Through the VPN
You will have options to choose:
- Choose Apps: Select specific applications that should use the VPN connection. For instance, you might route your browser and email client through the VPN for added security while leaving your streaming app to use the direct connection for better speed.
- Choose Websites: Some VPNs allow URL-based split tunneling. You can set specific websites to bypass the VPN, which can be handy for accessing local content while securing sensitive data.
How to Choose Which Traffic Goes Through the VPN?
Choosing which traffic to route through the VPN depends on your needs. Here are some considerations to help you decide:
- Security Needs: Route sensitive activities like online banking, work-related tasks, and email through the VPN. This ensures your data stays encrypted and your IP address is hidden.
- Performance Requirements: For high-bandwidth activities like gaming or streaming, consider bypassing the VPN to avoid any speed reductions caused by encryption processes.
- Access to Local Services: If you need to access local websites or services that may block VPNs, set those apps or sites to bypass the VPN.
- Device-Specific Decisions: For devices that handle confidential and routine activities, like a smartphone or laptop, split tunneling can be of great use to one who wants to balance security and functionality.
VPN split tunneling strategically provides privacy and security for important tasks while allowing for the speed and convenience of regular internet. Setting up the VPN’s split tunneling feature wisely is crucial to enhance your online experience.
FAQs : VPN Split Tunneling
1. Can Split Tunneling Expose My Data?

Yes, split tunneling can expose some of your data if it’s not configured properly. In split tunneling, out of the two possibilities, you benefit from protecting the encrypted tunnel for only the traffic going through the VPN.
Traffic that passes through the VPN excludes remains open to threats such as hacking, spying, or data interception. To minimize the risk, make sure that sensitive activities like online banking or work-related tasks are always routed through the VPN.
2. Does Split Tunneling Work on Mobile Devices?
Yes, split tunneling is possible in many mobile operating systems, including Android and iOS. However, the service and connection setups can differ between providers.
Some VPN apps let you configure split tunneling, in which you can choose which app uses the VPN and which does not.
The process for enabling split tunneling varies depending on the VPN provider; it is, therefore, crucial to consult your service provider to conduct it correctly.
3. Can Split Tunneling Be Used for Streaming?

Split tunneling has been used for streaming purposes. This method allows you to keep your streaming apps faster while bypassing any local content restrictions.
This is especially handy if you wish to stream content that is limited to your region but want to protect other operations with the VPN.
Just make sure that the VPN of your preference supports split tunneling and is compatible with your streaming applications.
4. Is VPN Split Tunneling Secure?
VPN split tunneling can be secure if used wisely, but it does involve some risks. It offers selective encryption, allowing you to protect only the traffic that needs it most. However, any traffic that bypasses the VPN is not encrypted and could be exposed to cyber threats.
To maximize security, always ensure your sensitive data and activities are routed through the VPN and keep your split tunneling settings up-to-date.